File size: 24.3 MB
经典设备背景
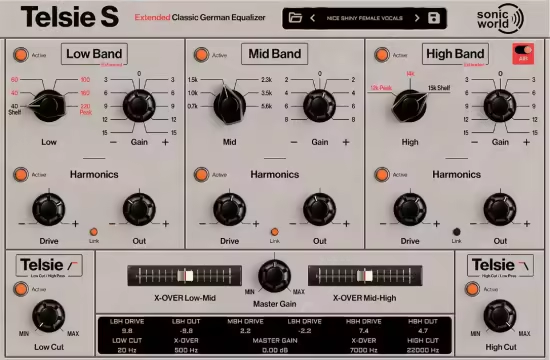
西门子 W295b 与 Telsie S 的核心功能
0.7 kHz、1 kHz、1.5 kHz、2.3 kHz、3.5 kHz、5.6 kHz,最大提升与衰减幅度均为 8 dB。
该峰值滤波器具备比例 Q 值特性 —— 提升或衰减的 dB 值越大,钟形滤波曲线的宽度越窄。
Telsie S 插件的额外优势
1. 新增低频段滤波频率
40 Hz、60 Hz、100 Hz、160 Hz、220 Hz。
2. 新增高频段滤波频率与 AIR 开关
3. 谐波功能
- Drive 旋钮:调节添加的谐波量,丰富信号质感;
- Out 旋钮:补偿因 Drive 调节导致的音量增益;
默认状态下两个参数相互联动,可通过 Link(联动)开关关闭该功能。
4. 低切 / 高通与高切 / 低通滤波器
- 例如:可通过低切滤波器轻松减少原声吉他或人声轨道中的低频轰鸣,或通过高切滤波器切除刺耳的高频噪声;
- 也可同时使用两种滤波器,为其他轨道预留频率空间。
截止频率可自由选择,两款滤波器均采用 -12 dB / 倍频程的平缓斜率。
5. 频段交叉点调节(低 – 中 / 中 – 高)
- 可在低频段大幅提升 220 Hz 及以下频率,为人声奠定扎实基础;若将低 – 中交叉点从 500 Hz 下调至 400 Hz,还能切除 400 Hz 以上的多余频率;
- 对于高频段,若将中 – 高交叉点设置为高于 7 kHz,即可在大幅提升高频的同时,避免增强 7 kHz 处的多余噪声。
(配图说明 2:线性字母数字控制面板,含白色滑块与红色竖线,下方标注 “X-OVER Mid-High”(中 – 高频段交叉点))
6. 主增益与参数栏
- 三个频段的谐波参数(LBH:低频段谐波、MBH:中频段谐波、HBH:高频段谐波);
- 低切 / 高切滤波器参数;
- 两个交叉点的选定频率;
- 主增益数值。
The SonicWorld Telsie S is a 3-band equalizer plug-in based on the famous Siemens W295b discrete class A equalizer from the 1970s.
The W295b is known for its wonderfully airy highs and voluminous bass. Telsie S delivers this sound, along with some very useful upgrades compared to its analog counterpart!
Designed and built for the ARD (Association of German Public Broadcasters) in the 70´s, the Siemens mixing consoles reflected what was technically feasible at the time and were at the cutting edge of technology.
These mixing consoles were the direct successor for the tube-based V72/V76 mixing consoles.
Highly sought-after modules like the V276 Microphone Preamp and the W295 Series Equalizer were used in these consoles.
Siemens offered 3 different Equalizer versions: The W295, the W295a and the W295b which has the most elaborated design of the 3 models.
All these models share a low-shelf filter and high-shelf filter, while only the W295b features a mid-band with a presence/absence filter.
The W295b is still today the secret weapon of many engineers as it provides these VERY nice airy highs ….
At SonicWorld we know this analog marvel very well, as we have been servicing and racking many of these units in the last 20 years.
Interior of vintage Siemens W 295B Equalizer showing electronic components and control knobs.
Now you can have that sound without the crackle of old switches, dried-out capacitors, hard-to find transistors, etc.
The features of the Siemens W295b and Telsie S
Similar to the original hardware device, the Telsie S is a three-band equalizer with shelf-filters on the high and low bands and a peak filter on the mid band. The low-shelf filter has its ±15 dB point at 40 Hz, while the high-shelf filter has its ±15 dB point at 15 kHz.
The mid-band is a presence/absence filter with Peak characteristics and 6 selectable center frequencies
0.7 kHz, 1 kHz, 1.5 kHz, 2.3 kHz, 3.5 kHz, and 5.6 kHz, and a maximum boost and cut of 8 dB each.
This peak filter has a proportional Q factor. This means that the width of the bell narrows the more dB you boost or cut.
The additional benefits of the Telsie S plug-in
Low Band Filter with additional frequencies
As an alternative to the original device’s low-shelf filter at 40 Hz, there are additional peak filter frequencies with center
frequencies at 40, 60, 100, 160 and 220 Hz.
These peak filters have a proportional Q factor, meaning the width of the bell narrows the more dB you boost or cut.
These additional peak filter frequencies give you significantly more sonic possibilities than the original shelf filter at 40 Hz.
High Band Filter with additional frequencies and AIR switch
The high band features the original device’s super nice- sounding high-shelf filter at 15 kHz. As an alternative Telsie S also offers two additional peak filters with center frequencies at 12 kHz and 14 kHz, with a maximum boost or cut of 15 dB in 3 dB steps.
The AIR switch significantly extends the high band’s frequency response. You can experiment with running your session at a higher sample rate to make this effect even more noticeable
Harmonics function
Each of the three equalizer bands has a harmonics function with two parameters: Drive and Out.
The Drive control allows you to adjust the amount of harmonics added to enrich the signal.
You can use the Out control to compensate for the increase in volume caused by the Drive section.
The two parameters are linked by default. You can disable this by using the Link switch.
Be careful when you do this as extreme boosts or cuts are possible.
Extreme boosts could not only harm your ears, but also your equipment.
We do not take responsibility for any potentional damage.
Low Cut/ High Pass and High Cut/Low Pass Filter
The Low Cut (High Pass) and the High Cut (Low Pass) filters are used to clean up the frequency range of your signal .
For example low rumble on an acoustic guitar or vocal track can be easily reduced with the Low Cut, or you can cut the high-frequency range for nasty frequencies.
Or with using both filters to give room for other tracks.
The cutoff frequency is freely selectable, both filters have a gentle slope of -12 dB per octave.
X-OverS Low Band/Mid Band and Mid Band/High Band
On the analog W295b, the high and low band curves are extremely broad. This means that a boost or cut in the 40 Hz shelf band has a sonic impact up to approximately 2 kHz. With the 15 kHz shelf band, a boost or cut has a sonic impact starting at around 200 Hz.
This characteristic never sounded appealing to us, as it often results in unwanted processed frequency ranges, even if you only want to boost or cut at much higher or lower frequencies.
This is where the two X-Over frequency controls come into play.
These allow you to set the respective frequency at which the Telsie S’s three equalizer bands merge.
The factory default crossover frequencies for the two crossover frequency controls are 500 Hz and 7 kHz.
This lets you give the presence band more space, even if you don’t want to boost or cut anything in this frequency range.
A close-up of a vintage control slider labeled “X-OVER Low-Mid” with a white knob and red indicator line, set at the middle position.
A linear alphanumeric control panel with a white slider and a red vertical line and the text ‘X-OVER Mid-High’ below.
This is very helpful for significantly influencing the equalizer curves and finding the right sound for different EQ requirements. You can boost for example with the low band a good amount at 220Hz or lower to give vocals a good basis and you can cut off unwanted higher frequencies at 400 Hz if you lower the X-over from 500 Hz down to 400 Hz.
The same goes for the high band. You can massively boost the high frequencies and avoid boosting unwanted frequencies at 7k if you set the X-Over Mid-High to a higher value than 7 kHz.
Try our EQ presets to find out how useful this feature is!
Master Gain and Parameter Bar
The Master Gain is used to compensate for level differences caused by equalization or harmonics.
Clicking the Master Gain control resets it to 0 dB.
The Parameter Bar displays the set values of the three harmonics bands LBH (Low Band Harmonics), MBH (Mid Band Harmonics), HBH (High Band Harmonics), the Low- and High-Cut filters, the chosen frequencies of the two X-overs and the Master Gain.